Completion
Complete each
statement.
|
|
|
1.
|
In a process known as ____________________, eroded materials are dropped in
another location.
|
|
|
2.
|
A major problem in farming areas is _________________________, which is the
deepening and widening of rill channels.
|
|
|
3.
|
A(n) _________________________ is a distinct layer, or zone, within a soil
profile.
|
|
|
4.
|
____________________ is the removal and transportation of weathered material
from one location to another.
|
|
|
5.
|
The process by which rocks on or near Earth’s surface break down and
change is ____________________.
|
|
|
6.
|
_________________________ is the erosion by running water of a small channel on
the side of a slope.
|
Short Answer
|
|
|
7.
|
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
|
|
|
8.
|
What is acid precipitation and how does it affect the weathering process?
|
|
|
9.
|
Give an example of how animals, including humans, affect the erosional
process.
|
|
|
10.
|
Describe how soils form layers.
|
|
|
11.
|
Below is a picture of a soil profile. Compare the characteristics of soil in
Horizon A with soil in Horizon B. 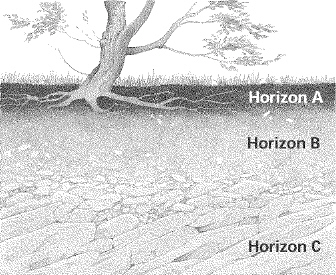
|
|
|
12.
|
How does climate influence the rate of weathering of earth materials?
|
|
|
13.
|
Describe how soil forms.
|
|
|
14.
|
How do living things impact weathering and erosion?
|
|
|
15.
|
Contrast mechanical and chemical weathering, and give examples of each.
|
|
|
Study the diagram. Then answer the following questions. 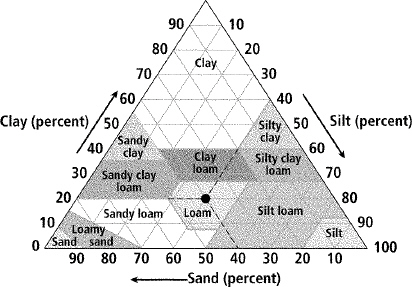
|
|
|
16.
|
What property of soil does the diagram illustrate?
|
|
|
17.
|
Name the three sizes of soil particles, from largest to smallest.
|
|
|
18.
|
How would you classify a soil that contains 60 percent sand, 30 percent silt,
and 10 percent clay?
|
|
|
19.
|
How would you classify a soil that contains equal percentages of all three sizes
of soil particles?
|
|
|
20.
|
About what proportion of sand/silt/clay makes up sandy clay?
|
|
|
21.
|
In general, soil drainage is determined by particle size: the larger the
particle size, the better the drainage. Compare the drainage of sand, sandy clay, and clay
soils.
|
Problem
|
|
|
A golf course designer, who is about to build a championship golf course, has
come to you with a problem. He tells you that parts of his developing course cannot grow grass and
tend to flood. After testing the soil, you decide that the reason it drains poorly and doesn’t
retain adequate moisture is because it has too much nonporous clay. You tell him that by adding soil
conditioners, the new soil will improve its drainage and retain more water. You mention that water
retention is important because water supplies are low in the hot summer months, and grasses need
water to stay green. Improved drainage will also allow more rainfall to be soaked into the soil, thus
lessening runoff and water erosion. You develop a simple setup to test various soil
combinations for drainage and water retention. You will add dry soil, which was heated to expel all
moisture, to a beaker. The beaker has a drain hole in the bottom to allow the drainage of excess
water to a measuring cylinder. You add 200 ml of water to the beakers with the various soil
combinations. After one hour, you then reweigh the soil and measure the drainage water. The
clay is the unsuitable soil from the golf course. Humus and sand were picked up from a local nursery,
and soils A and B are higher priced synthetic soils produced by a chemical company. Most of the soil
combinations drained in less than 30 minutes. When the drain time is greater than 60 minutes, this
indicates poor drainage and some of the water will remain on top of the soil, where it either
evaporates or runs off. All water weights are given in grams. One gram of water is approximately
equal to one milliliter. 
| | Clay | Clay +
Humus | Clay
+
Sand | Clay +
Soil A | Clay +
Soil B | | Dry soil weight | 600 g | 600 g | 600 g | 600 g | 600 g | | Water added | 200 g | 200 g | 200 g | 200 g | 200 g | | Wet soil weight | 690 g | 730 g | 640 g | 730 g | 760 g | | Water drainage | 20 g | 70 g | 160 g | 70 g | 35 g | | Time to drain | >60 min | 30 min | 20 min | 30 min | >60 min | | | | | | |
|
|
|
22.
|
The water added to the dry soil should equal the weight of the wet soil plus the
drainage weight. If it doesn’t, it’s because some of the water evaporated or ran off.
Using the data from the chart provided above, complete the table below by indicating the amount of
water that either evaporated or ran off. | | Clay | Clay +
Humus | Clay
+
Sand | Clay +
Soil A | Clay +
Soil B | Water
evaporated/runoff | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
23.
|
Compare the use of sand and humus as far as their ability to retain water and
improve drainage.
|
|
|
24.
|
How does Soil A and B compare to humus as far as their ability to retain water
and improve drainage.
|
|
|
25.
|
Why do you suppose clay has such a high evaporation rate?
|
|
|
26.
|
Why is sand not a good soil conditioner?
|
|
|
27.
|
What soil combination would you recommend to the golf course designer? What are
some other factors that might influence the selection of the best soil conditioner?
|