Modified True/False
Indicate
whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the
statement true.
|
|
|
1.
|
Herd animals are usually concentrated in the forest biome.
_________________________
|
|
|
2.
|
The great northern coniferous forests are part of the tundra biome.
_________________________
|
|
|
3.
|
Light intensity is a major limiting factor of the tundra biome.
_________________________
|
|
|
4.
|
Phytoplankton, which obtain energy by photosynthesis, are usually found
concentrated in the photic zone of the ocean. _________________________
|
|
|
5.
|
A pioneer community is usually the stable result of succession.
_________________________
|
|
|
6.
|
Optimal factors restrict the numbers of organisms that can exist.
_________________________
|
|
|
7.
|
Age, physical condition, and stage in its life cycle may all influence an
organism's limits of tolerance. _________________________
|
|
|
8.
|
The range of factors under which an organism functions and survives is known as
a limiting factor. _________________________
|
|
|
9.
|
The tundra is a region dominated by deciduous trees.
_________________________
|
|
|
10.
|
A large group of ecosystems characterized by the same type of climax community
is called a taiga. _________________________
|
|
|
11.
|
The colonization of new sites by communities of organisms is secondary
succession. _________________________
|
|
|
12.
|
A pioneer community is a stable, mature community that undergoes little
or no succession. _________________________
|
|
|
13.
|
Conditions that restrict the existence, population size, reproductive success,
or distribution of organisms are called ranges of tolerance. _________________________
|
|
|
14.
|
The portion of the shoreline that is affected by high and low tides is the
aphotic zone. _________________________
|
|
|
15.
|
The region of the ocean shallow enough for sunlight to penetrate is the
photic zone. _________________________
|
|
|
16.
|
Succession is the replacement of one community by another as
environmental conditions change. _________________________
|
|
|
17.
|
A body of water near the coast that is partly surrounded by land and contains
both fresh and salt water is known as the intertidal zone. _________________________
|
|
|
18.
|
Humus is a layer of soil that remains frozen throughout the year.
_________________________
|
|
|
19.
|
Microscopic organisms that float in the sunlit regions of the ocean are
pioneer species. _________________________
|
|
|
20.
|
The tundra is an arid region characterized by little or no plant life.
_________________________
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
21.
|
An uncut lawn becomes a meadow and eventually a forest. This process is an
example of _____.
a. | aphotic zones | c. | estuary | b. | primary succession | d. | secondary
succession |
|
|
|
22.
|
A girl notices that her guppies reproduce most when her fish tank water is
slightly alkaline. They stop reproducing if the water becomes acidic or if the water becomes too
alkaline. This is an example of _____.
a. | secondary succession | c. | communities | b. | zones of tolerance and
intolerance | d. | intertidal
zones |
|
|
|
Ling feeds her guppies one-half teaspoon of fish food every day. The average
guppy population in her aquarium over a four-month period is 38 guppies. She increased the food to
one teaspoon per day. After a four-month period, the average population is 53 guppies.
|
|
|
23.
|
Which of the following statements is supported by these data?
a. | The size of the aquarium was a limiting factor. | b. | One-half teaspoon of
food was a limiting factor. | c. | As long as Ling keeps adding more food, the
guppy population will continue to grow. | d. | Guppies reproduce
rapidly. |
|
|
|
24.
|
When Ling increased the amount of food, what happened to the carrying capacity
of the aquarium?
a. | It increased. | c. | It remained the same. | b. | It
decreased. | d. | It increased and
then decreased. |
|
|
|
25.
|
The stable ecosystem that develops due to succession _____.
a. | is called a niche | c. | is called a climax community | b. | is always a
forest | d. | never
changes |
|
|
|
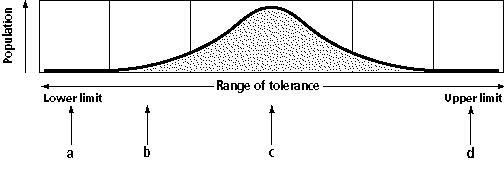 Figure
3-3
|
|
|
26.
|
In Figure 3-3, where will you be most likely to find the greatest
diversity?
|
|
|
27.
|
In Figure 3-3, which section would have a lack of organisms due to an
overabundance of resources?
|
|
|
28.
|
In Figure 3-3, which section would account for a lower number of organisms near
the bottom of a pond due to a short supply of oxygen and sunlight?
|
|
|
29.
|
What type of succession is most likely to happen in Figure 3-4? 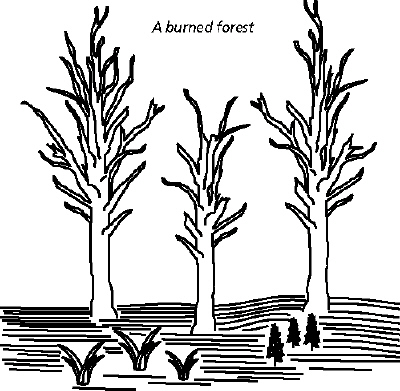 Figure 3-4 a. | primary | c. | teriary | b. | secondary | d. | climax |
|
|
|
30.
|
If you released a new species of deer into each of the stages shown in Figure
3-5, in which stage would the species be most successful? Figure 3-5
|
|
|
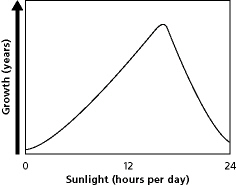 Figure
3-6
|
|
|
31.
|
Look at the graph in Figure 3-6. What does this graph tell us about this species
of plant?
a. | too much sunlight can hurt them | c. | heat is damaging to
them | b. | they thrive in a lot of sun | d. | they need plenty of water |
|
|
|
32.
|
Look at the graph in Figure 3-6. Approximately how many hours of sunlight should
these plants receive each day in order to make them grow at their optimum level?
|
|
|
33.
|
What would be the best time of the year to plant the organism described in
Figure 3-6?
a. | winter | c. | summer | b. | spring | d. | fall |
|
|
|
 Figure
3-7
|
|
|
34.
|
You take a sample of species from the area labeled A in Figure 3-7. What would
you expect to find?
a. | almost no life | c. | organisms that need very little oxygen | b. | great species
diversity | d. | one dominant
species of fish |
|
|
|
35.
|
What type of species would be most likely found in the area labeled D in Figure
3-7?
a. | one that requires plenty of oxygen | b. | plants that require light | c. | amphibians that need
a warm habitat | d. | decomposers that feed on dead organisms |
|