True/False
Indicate whether the
statement is true or false.
|
|
|
1.
|
Balanced forces acting on an object cause the object to accelerate.
|
|
|
2.
|
Gravity causes all falling objects to accelerate at a rate of 98
m/s2.
|
|
|
3.
|
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of position.
|
|
|
4.
|
The momentum of a 5,000-kg truck that is standing still is greater than the
momentum of a 3,000-kg truck that is also at rest.
|
|
|
5.
|
The projectile velocity is the highest velocity that will be reached by a
falling object.
|
|
|
6.
|
When an object falls, it is reacting to the force of gravity.
|
|
|
7.
|
Jane is on a merry-go-round that is moving at a constant speed. Her velocity is
also constant.
|
|
|
8.
|
Momentum is a property of an object and cannot be transferred from that object
to another object.
|
|
|
9.
|
Objects in Earth's orbit appear to be weightless because they are in free
fall.
|
|
|
10.
|
Friction is a force that encourages motion between two surfaces that are
touching each other.
|
Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
11.
|
The upward force on an object falling through the air is ____.
a. | air resistance | c. | momentum | b. | inertia | d. | terminal
velocity |
|
|
|
12.
|
The relationship among mass, force, and acceleration is explained by
____.
a. | conservation of momentum | c. | Newton's second law of
motion | b. | Newton's first law of motion | d. | Newton's third law of
motion |
|
|
|
13.
|
A feather will fall through the air more slowly than a brick because of
____.
a. | air resistance | c. | inertia | b. | gravity | d. | momentum |
|
|
|
14.
|
In the absence of air, a penny and a feather that are dropped from the same
height at the same time will ____.
a. | fall at different rates | c. | float | b. | fall at the same
rate | d. | not have
momentum |
|
|
|
15.
|
The acceleration due to gravity is ____.
a. | 98 m/s2 | c. | 9.8 m/s | b. | 9.8 m/s2 | d. | 0.98 m/s |
|
|
|
16.
|
According to Newton's second law of motion, ____.
a. | F = m ´ a | c. | F = p
´ a | b. | F = m ´
v | d. | F =
p ´ v |
|
|
|
17.
|
When an object moves in a circular path, it accelerates toward the center of the
circle as a result of ____.
a. | centripetal force | c. | gravitational force | b. | frictional force | d. | momentum |
|
|
|
18.
|
The path of a projectile is ____.
a. | curved | c. | always vertical | b. | always horizontal | d. | straight |
|
|
|
19.
|
For any object, the greater the force that's applied to it, the greater its
____ will be.
a. | acceleration | c. | inertia | b. | gravity | d. | velocity |
|
|
|
20.
|
The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their
____.
a. | frictional forces | b. | inertia | c. | masses and the
distance between them | d. | speed and
direction |
|
|
|
21.
|
As you get farther from the center of Earth, your weight will ____.
a. | decrease | c. | remain the same | b. | increase | d. | can't tell from information
given |
|
|
|
22.
|
When a force is exerted on a box, an equal and opposite force is exerted by the
box. These forces are called ____ forces.
a. | action-reaction | c. | frictional | b. | centripetal | d. | gravitational |
|
|
|
23.
|
A real car moving at 10 km/h has more momentum than a toy car moving at the same
speed because the real car ____.
a. | generates less friction | c. | has less mass | b. | has greater
mass | d. | has greater forward
motion |
|
|
|
24.
|
In the equation p = m ´ v,
the p represents ____.
a. | friction | c. | momentum | b. | inertia | d. | position |
|
|
|
25.
|
The statement "to every action there is an equal and opposite
reaction" is ____.
a. | the law of conservation of momentum | b. | Newton's first law of
motion | c. | Newton's second law of motion | d. | Newton's third law of
motion |
|
|
|
26.
|
The unit of momentum is ____.
a. | kg ´ m | c. | kg ´ m/s2 | b. | kg ´
m/s | d. | m/s2 |
|
|
|
27.
|
When two balls collide, the momentum of the balls after the collision is
explained by ____.
a. | the law of conservation of momentum | b. | Newton's first law of
motion | c. | Newton's second law of motion | d. | Newton's third law of
motion |
|
|
|
28.
|
A 300-N force acts on a 25-kg object. The acceleration of the object is
____.
a. | 7,500 m/s2 | c. | 25 m/s2 | b. | 300 m/s2 | d. | 12
m/s2 |
|
|
|
29.
|
A 3,000-N force acts on a 200-kg object. The acceleration of the object is
____.
a. | 50 m/s2 | c. | 15 m/s2 | b. | 26 m/s2 | d. | 150
m/s2 |
|
|
|
30.
|
An object that is in free fall seems to be ____.
a. | not moving | c. | speeded up by air resistance | b. | slowed by air
resistance | d. | weightless |
|
|
|
31.
|
If gravity did NOT affect the path of a horizontally thrown ball, the ball would
____.
a. | go straight up | c. | follow a curved path | b. | fall straight down | d. | travel
horizontally |
|
|
|
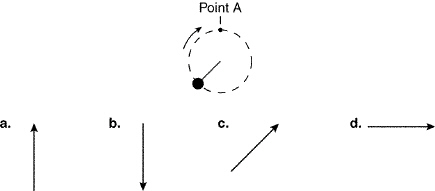 Figure
3-1
|
|
|
32.
|
A ball attached to a string is being swung in a clockwise circular path as shown
in Figure 3-1. Assume the string breaks at point A. In which direction will the ball be traveling an
instant later?
a. | direction a | c. | direction c | b. | direction b | d. | direction d |
|
|
|
33.
|
A ball attached to a string is being swung in a clockwise circular path as shown
in Figure 3-1. In which direction will the acceleration on the ball be when the ball passes point
A?
a. | direction a | c. | direction c | b. | direction b | d. | direction d |
|